Stimulating a Depolarized TC Neuron
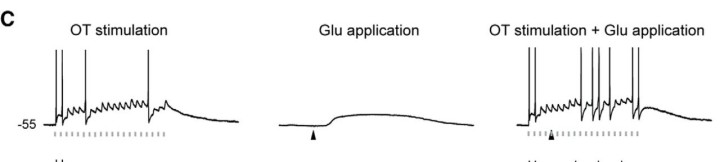
This figure shows how glutamate stimulation lifts the TC Neuron’s membrane potential so that more action potentials are generated. The graph at left shows action potentials when Dr. Augustinaite stimulated the incoming retinal axons without glutamate application to the neuron. In the center graph, the change in voltage shows an NMDA spike/plateau after Dr. Augustinaite applied glutamate to the dendrites of the TC neuron. This shows that that cortical input lifts the membrane potential towards stronger depolarization. The far right graph shows the first two procedures combined: Dr. Augustinaite stimulated the neuron with glutamate to create an NMDA spike/plateau and the neuron was more sensitive to incoming retinal stimulation, generating more action potentials, which then travel to the cortex.
Copyright OIST (Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University, 沖縄科学技術大学院大学). Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
Tags