Figure 4: Distance estimation in the parietal cortex utilizes dynamic Bayesian inference
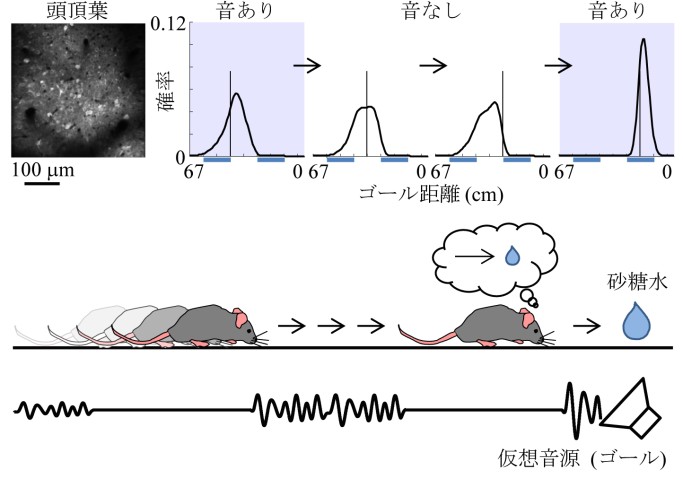
Figure 4: Distance estimation in the parietal cortex utilizes dynamic Bayesian inference
Probabilistic neural decoding allows for the estimation of the goal distance from neuronal activity imaged from the parietal cortex. Neurons could predict the goal distance even during sound omissions. The prediction became more accurate when sound was given. These results suggest that the parietal cortex predicts the goal distance from movement and updates the prediction with sensory inputs, in the same way as dynamic Bayesian inference.
Probabilistic neural decoding allows for the estimation of the goal distance from neuronal activity imaged from the parietal cortex. Neurons could predict the goal distance even during sound omissions. The prediction became more accurate when sound was given. These results suggest that the parietal cortex predicts the goal distance from movement and updates the prediction with sensory inputs, in the same way as dynamic Bayesian inference.
Copyright OIST (Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University, 沖縄科学技術大学院大学). Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
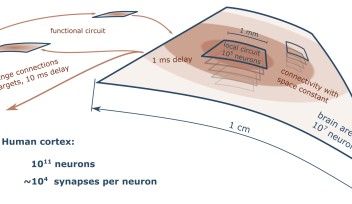
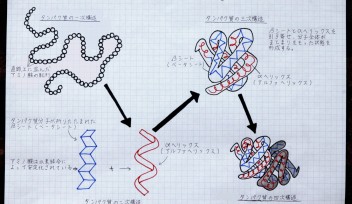
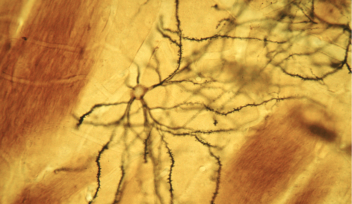
Tags